Intelligenza artificiale e megadati
Highlights
- Report / Paper / Summary4December2025Artificial Intelligence comes with both benefits and risks. Safe AI use that accounts for fundamental rights is thus crucial. While the 2024 EU AI Act was a milestone in this regard, its broad definitions regarding AI systems and high-risk AI could introduce loopholes for fundamental rights compliance. This report offers an empirical basis for much-needed practical guidance on the Act’s implementation. Based on interviews with AI developers, sellers, and users, FRA addresses challenges of its use in critical domains, like asylum, education, and employment. Our findings help guide next steps in realising the AI Act’s potential to ensure responsible innovation.
- VideoIn an increasingly digital world, tech advances affect almost all aspects of our lives and our rights. This FRF theme tackles topics such as regulating digitalisation without stifling innovation or surveillance-based advertising. Notable speakers include Catherine De Bolle, Executive Director at EUROPOL, Daniel Howden, Founder and Director of Lighthouse Reports, Nanna-Louise Linde, Vice-President for European Government Affairs at Microsoft, Alexandria Walden, Global Head of Human Rights at Google, among others.
- Report / Paper / Summary8December2022Artificial intelligence is everywhere and affects everyone – from deciding what content people see on their social media feeds to determining who will receive state benefits. AI technologies are typically based on algorithms that make predictions to support or even fully automate decision-making.
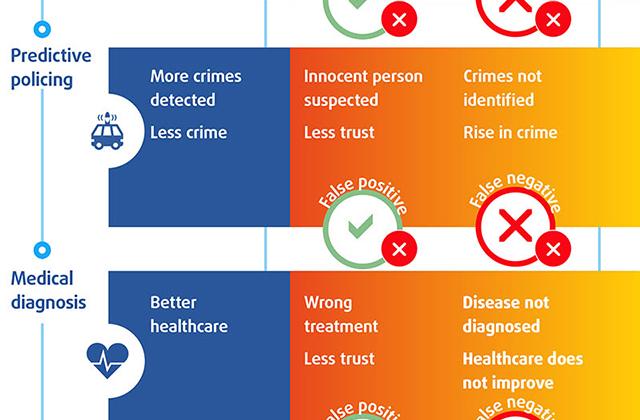
- Report / Paper / Summary14December2020Artificial intelligence (AI) already plays a role in deciding what unemployment benefits someone gets, where a burglary is likely to take place, whether someone is at risk of cancer, or who sees that catchy advertisement for low mortgage rates. Its use keeps growing, presenting seemingly endless possibilities. But we need to make sure to fully uphold fundamental rights standards when using AI. This report presents concrete examples of how companies and public administrations in the EU are using, or trying to use, AI. It focuses on four core areas – social benefits, predictive policing, health services and targeted advertising.